The internet, as we commonly interact with, represents just a fraction of the entire digital landscape. What we typically refer to as the "surface web" includes websites and content that are indexed by search engines, easily accessible through standard browsers. Beyond the surface web lies a much larger realm known as the "deep web." Furthermore, nested within the deep web is a smaller, intentionally concealed section known as the "dark web."
_1706592624.png)
The surface web covers less than 1% of the total internet; the majority is covered by deep web (almost 90%) and the remaining is dark web.
The dark web holds the dark realities of our societies. From illegal drug trade, human trafficking, arms dealings to planning terrorist attacks and making and selling child porn, dark web is hidden online market place for everything. The research suggests that over 50% of the websites on dark web are used for illegal activities. Our personal information such as passwords, photos and security numbers are frequently up for sale in some of these dark websites more often than you think.
The dark web gained a little spotlight when the mother of all breaches was uncovered few days ago. More than 30 billion data records were found ‘for-sale’ on dark web. This not only raised questions about the privacy of our data but also about the legality of such trades.
This article has been penned down to put a bright spotlight on dark web, uncovering the truths about its discovery, use, and ethical concerns.
Understanding deep web and dark web:
Surface web is accessible to everyone. There is no data privacy and anonymity. Anyone with an active internet connection can access every bit of information on surface web. There were no secure communication channels and no data privacy. This inherits need of privacy and secure communication channel led to the birth of deep web.
The invention of dark web:
There is not a single person or organisation that built the concept of deep web; but a major portion of deep web- the onion router, was developed by U.S. Naval Research Laboratory in 1990s.
The initial work on what would become Tor (The Onion Routing/router) began in the mid-1990s with researchers like Paul Syverson, Michael Reed, and David Goldschlag felt the need of private internet connection for undertaking secret missions. So, they developed onion routing, where each layer is encrypted and decrypted like onion peeling. Hence, it was named as onion routing.
Working of deep web:
The aim of the onion network was to develop a protected network system, where internet can be accessed without revealing user’s identity. It's like sending a package through a series of mailboxes, each one with a different address. Each mailbox only knows the address of the next mailbox in the chain, not the final destination or the sender. This makes it very difficult for anyone to track where the package came from or where it's going.
The same is the case of onion routing. Through using onion routing, the user data is transmitted through a series of servers as intermediaries. This makes the data and the research anonymous.
However, US navel Research laboratory faced a severe challenge- the network could not be made entirely anonymous until it was made available to everyone. Oher wise, any thing with onion extension could be easily deemed as suspicious.
Hence, US Navel research laboratory had to made onion routing available to public.
This led to the birth of deep web.
The rise of dark web:
As the concept of deep web was made public, the concept of dark web also came to picture. The development of anonymity-enabling tools like Tor in the late 1990s laid the foundation for the dark web. The invention of Bitcoin in 2009 further provided a secure and untraceable payment system for dark web transactions. This facilitated illegal activities, like drug and weapon sales and child pornography to flourish without traditional financial intermediaries, like banks.
Birth and demise of silk route:
Two years later, a dark web place for various illegal goods, the silk route, marked a pivotal point in the dark web arena. Drugs, weapons, hacking tools, you name it – it was all on sale. Data encryption made suppliers and customers anonymous and cryptocurrency made secure escrow payments. This not only diversified its application, but also raised the eyebrows of governmental organizations.
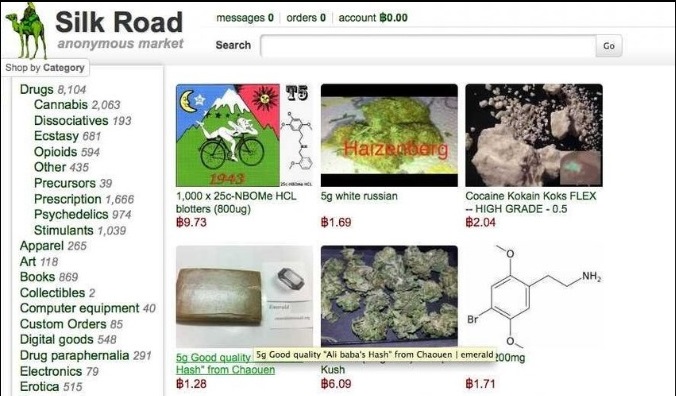
A year later, a security breach exposed Silk Route’s IP’s address. A year later, FBI seized two Silk Route servers from Iceland. The site's founder, Ross Ulbricht, made several critical mistakes, such as using unencrypted communication channels and logging into his account from a public library.
Combining the information from these key elements, authorities finally identified Ross Ulbricht. He was also known as "Dread Pirate Roberts.” He was found to be the mastermind behind the Silk Road. In October 2013, he was arrested in a San Francisco library.
After the silk route was shut down, severe copycat websites, such as silk route 2.0 and black market Reloaded, emerged. Although no market place could replace the sophistication of silk route, but the market became diversified. Many niche-specific markets emerged, which made it even more difficult to trace illegal activities in the fabric of dark web.
Conclusion:
The dark web remains a murky corner of the internet, whose future trajectory will depend on the ongoing struggle between those who seek to exploit it for illegal purposes and those who want to make it a safer and more secure space for everyone.
Copyright © 2026 getessayservice.com

.png)